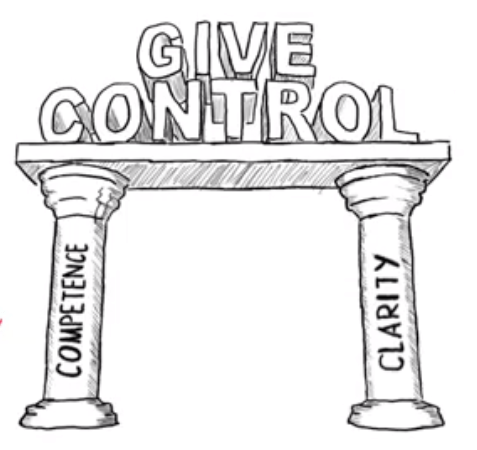
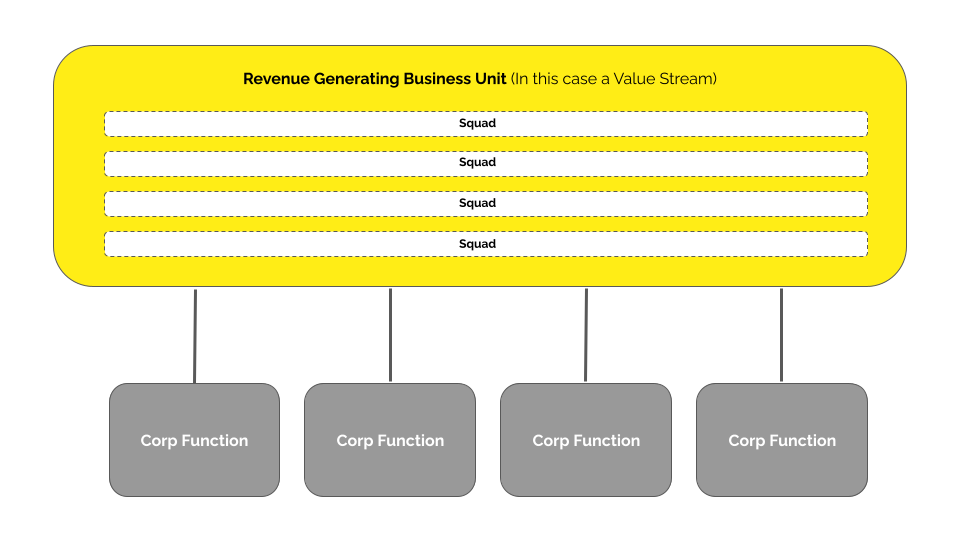
Many organisations have updated their revenue-generating business units' operating models to a value-stream or product-based model, increasing the flow of customer value and creating better business outcomes. However, updating the operating model of supporting corporate functions can also unlock significant value. Designing a corporate function operating model requires careful consideration and the work often differs significantly from designing the operating model of revenue-generating business units.
This article shares how we have approached this. We will refer to two different types of business units:
- Revenue-generating Business Units - a business unit that creates products or services that generate revenue.
- Corporate functions - business units that support revenue-generating business units, such as People and Culture, Marketing, Procurement, Corporate Affairs and External Communication, Finance and Commercial, Risk, Assurance, Legal and Compliance, and Sustainability.
Why are organisations focusing on corporate functions?
CEOs are looking to obtain better value from their corporate functions. According to Gartner, more value from corporate functions is one of the top three concerns of CEOs, jumping 63% among survey respondents.

There are three key reasons for this:
- There has been less investment in corporate functions. Many revenue-generating parts of organisations have invested to move to more end-to-end, value-stream-type operating models. The benefits they are enjoying are faster delivery, increased customer value flow, and better business outcomes.
- Corporate functions are not keeping up. Now that they are fast and lean, the revenue-generating business units have the same high service expectations for the corporate functions that support them. Yet, these corporate functions are working with operating models that have become outdated. The result is the creation of “shadow functions” within the revenue-generating business units as they seek greater control and faster results that are better aligned with their needs. While this short-term fix might solve their immediate issue, it does so at considerable cost to the organisation, creating inconsistency and waste. Ultimately, this can lead to confusion, politics, and organisational fragmentation.
- Pressure to improve organisational cost and efficiency. With less stable environments and more intense competition in many markets, there’s a mounting emphasis on performance results. At the time of writing, 75% of our customers have a cost reduction agenda. In addition, corporate profit margins are at their highest since the 1950’s, meaning there is little “headroom” for increasing revenue. One of the only places left to find profit is cost. These pressures are forcing corporate functions to:
- Boost operational excellence further, usually while reducing costs
- Consolidate and centralise duplicate roles and design engagement approaches that allow for speed and independence.
- Improve Governance, Planning & Prioritisation to continually ensure the most valuable work for the business is the focus and being delivered continuously.
In their attempt to achieve this, many corporate functions have flipped back and forth between centralised and decentralised models, often the result of incoming new leadership or on the advice of a consulting firm. Over time, they’ve become bloated, expensive, slow, and confused. In reaction to this, revenue-generating business units are left with little other option than to “opt-out” by creating shadow functions.
Finally, patchwork fixes are frequently applied to solve specific problems without the proper buy-in and change management or a greater understanding of the organisational context. As a result, over time there is diminished clarity and coherence of how everything works together, low ownership to maintain and champion the change, and often an unintended increase in complexity.
Through our work with executives and business leaders, we see recognition of the above, with increased focus on ensuring that corporate functions are set up to support organisational growth better. As a result, leaders are investing in increasing delivery speed within corporate functions.
Challenges
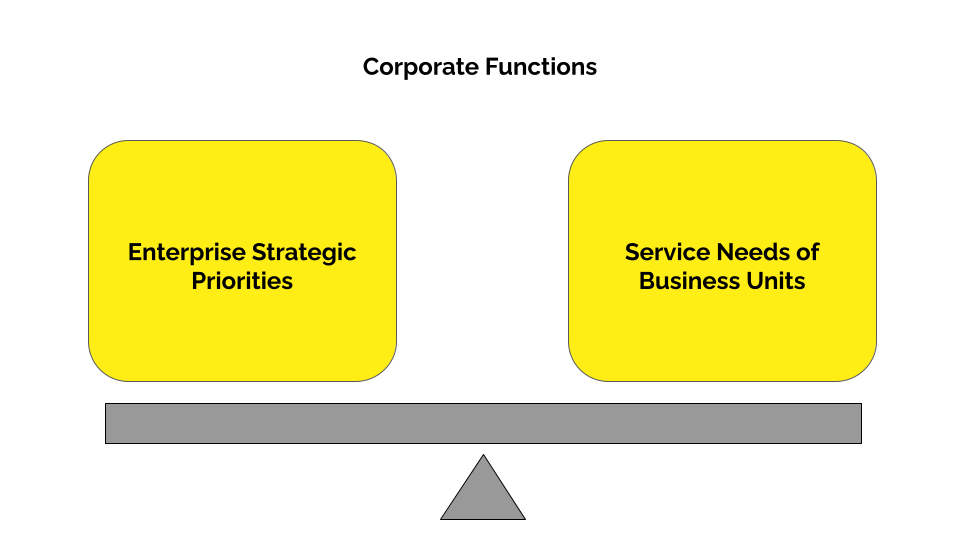
Corporate functions are often in a constant battle to balance their strategic priorities while also meeting the needs of the revenue-generating business units they serve. Tensions arise when these become imbalanced.
- If it is more weighted towards the enterprise's strategic priorities, the BUs feel that the corporate functions are adding more work and slowing them down, and in some cases, they prefer to work in isolation.
- If it is more weighted towards the needs of the business units, there is a lack of strategic coordination.
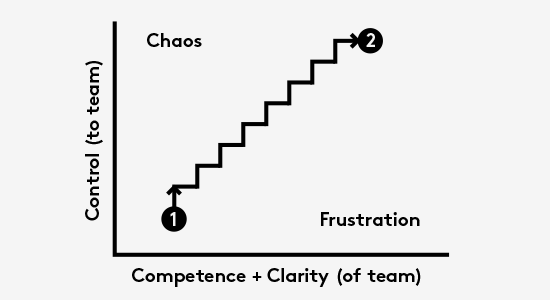
Knowing how to enable the right balance is essential but hard. The struggle to find this balance lies in three key pain points:
- Authority and decision rights - Is the ownership and decision-making authority with the revenue-generating business unit or the corporate function?
- Value definition and prioritisation—In a world where there’s always more work to be done than time or resources, it’s easy to misalign what work is valuable (and what isn’t) and whether/when/how the work is resourced. What is our definition of value?
- Expectations on services - Without intentional conversations and alignment, there is often a mismatch of what is expected from the revenue-generating business units (demand) and what is provided by the corporate function (supply) in terms of speed of delivery, level of expertise or contextual understanding, quality of work, level of ownership, type of engagement, etc.
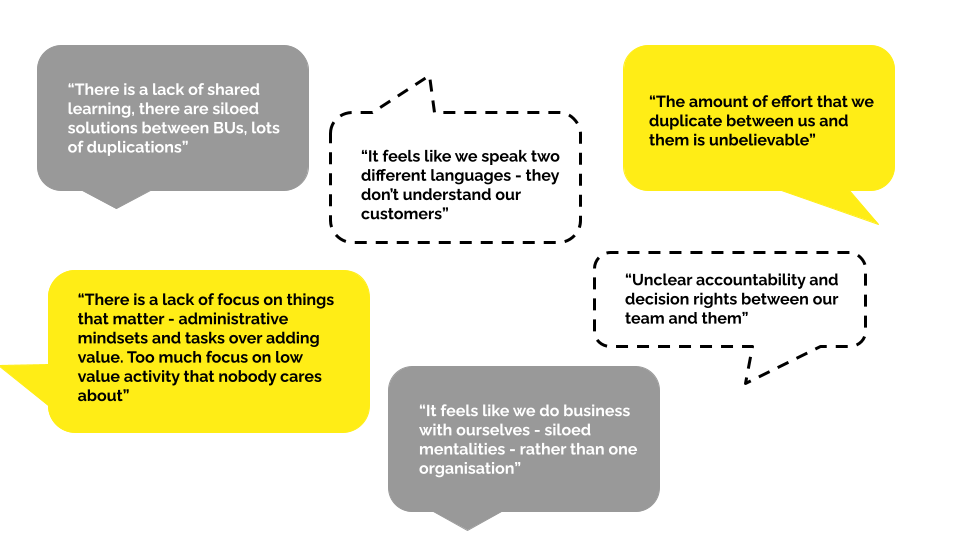
A reconfigured corporate function operating model is a holistic and systemic way to solve these challenges.
What is an Operating Model?
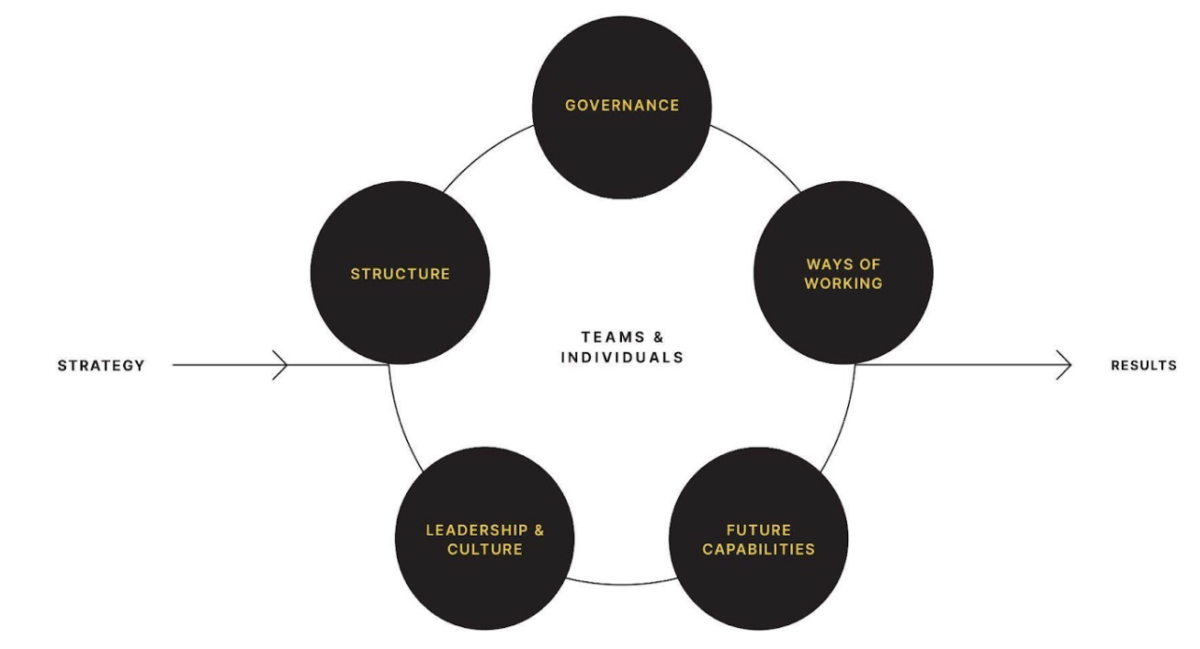
Simply put, an operating model helps teams and individuals turn strategy into results.
It is a framework that operationalises strategic plans by translating and managing the big-picture thinking into coordinated day-to-day actions needed to achieve tangible outcomes. An organisation’s operating model defines how their capabilities are managed to achieve their strategic goals, and the success of an organisation depends on the interconnectedness of five core elements.
- Governance: the framework used to plan and prioritise the work. It’s a critical process to align day-to-day work priorities with the organisational strategy so people can deliver results. It’s composed of a regular cadence of activities and events that breaks down the organisational strategy into long term objectives, then shorter term goals with tangible outcomes, then incremental plans on how to deliver.
- Ways of Working: the practices, processes, methodologies, and behaviours that guide how work is planned, executed, and managed. It provides clarity and consistency to how people collaborate, communicate, and execute their tasks to achieve organisational goals.
- Future Capabilities: these are the skills, processes, technologies, and structures that an organisation needs to develop or enhance in order to achieve its strategic goals and remain competitive in a changing environment. In an operating model, future capabilities act as enablers that allow an organisation to meet future challenges, seize new opportunities, and adapt to evolving market demands.
- Leadership & Culture: the behaviours, values, and practices set and demonstrated by leaders and embraced by the organisation. Together, they define the tone, environment, and mindset that drive how work gets done and how employees experience the organisation.
- Structure: in the context of an operating model, organisational structure refers to the framework that defines how tasks are divided, coordinated, and supervised within an organisation. It outlines how people and responsibilities are organised to achieve the organisation's strategic objectives and deliver its value proposition.
Structure brings all the elements together, and because it is also the most visible and tangible part of the operating model, it’s often easier to start with that, then integrate the other elements. However, Ways of Working are highly interconnected with Structure, so these must be front of mind during the design process.
Start with Strategy & Principles
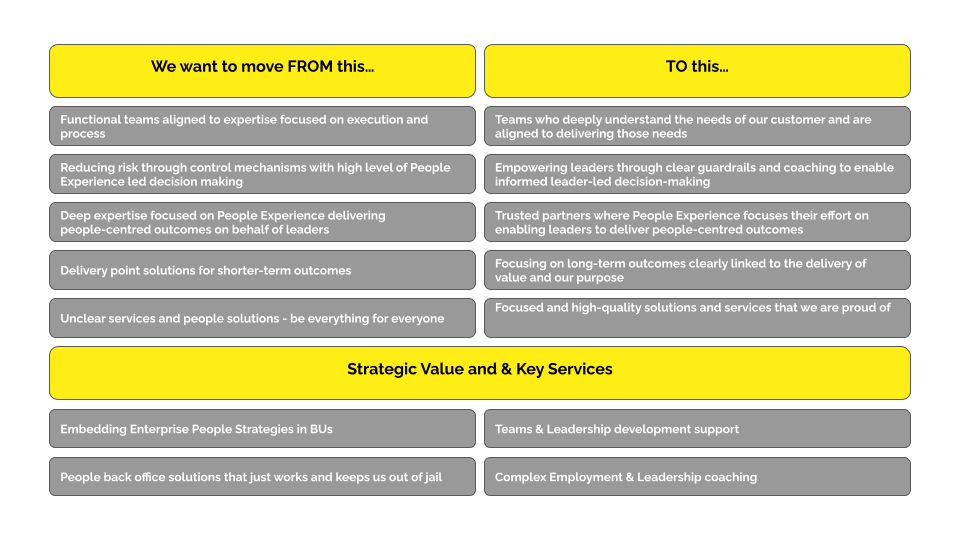
An operating model starts with the strategy so this needs to be right before moving into design, and Radically often helps clients relook at their strategy as a first step. With a corporate function, because its core purpose is to enable the Business Units to achieve the organisational strategy, a highly differentiated or clearly expressed strategy doesn’t need to be a prerequisite. Instead, it can be helpful to articulate clear shifts they want to target. Below is an example.
The Radically Teaming Model
Conventional hierarchical structures make it challenging to visualise how teams and their roles align with how they engage with their internal consumers. Often, our roles are made more complex and slow due to a lack of clarity on decision rights.
The Radically Teaming Model ensures consistency in how we discuss team structures and whether they enable or hinder our ability to get work done. By introducing distinct team and interaction types, we create clarity and focus on the organisational structures.
What is a Teaming Model?
Teaming models refer to organisations' frameworks or structures to form, manage, and optimise teams to achieve specific goals. These models provide guidelines on:
- How teams should be composed
- How they should operate
- How they should be supported to maximise their effectiveness.
Different teaming models are suited to different types of work and organisational needs. Teaming models help organisations maximise efficiency through:
- Improved resource utilisation
- Optimisation of skills allocation by aligning the right skills and expertise with the right tasks
- Flexibility to respond quickly to changes in workload or priorities
- Removing duplication
- Elimination of duplicate roles and tasks
- Standardised processes with clear ownership of implementation and maintenance
- Faster decision-making
- Clear roles and responsibilities, both within the function and between the function and its consumers
- Decision-making authority where the work happens
- Increased ownership and accountability
- Clear ownership of tasks based on how functions engage with and support their customers
- Ability to build feedback loops and monitor performance
Why use the Radically Teaming Model?
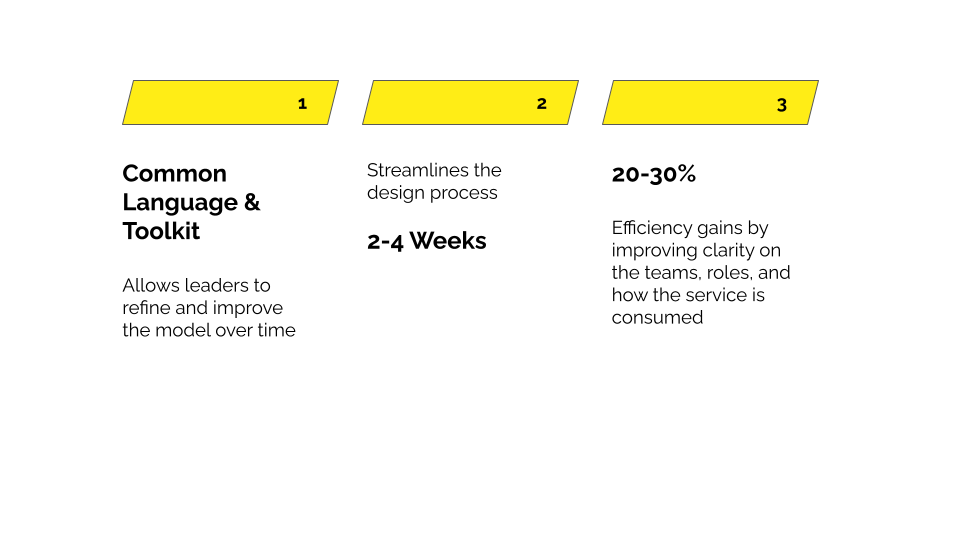
There are three key reasons why you should use a teaming model:
- It provides a common language and toolkit across the organisation, which builds clarity at scale and allows leads to refine and improve the model over time.
- It streamlines the design process from something that would take 3-6 months to 2-4 weeks. This means significantly reducing the cost and distraction of a longer design process and the ability to benefit from the new operating model sooner.
- Returns 20-30% efficiency gains by improving clarity on the teams, roles, and how the service is consumed.
Radically Teaming Model Components?
There are two components to the Radically Teaming Model:
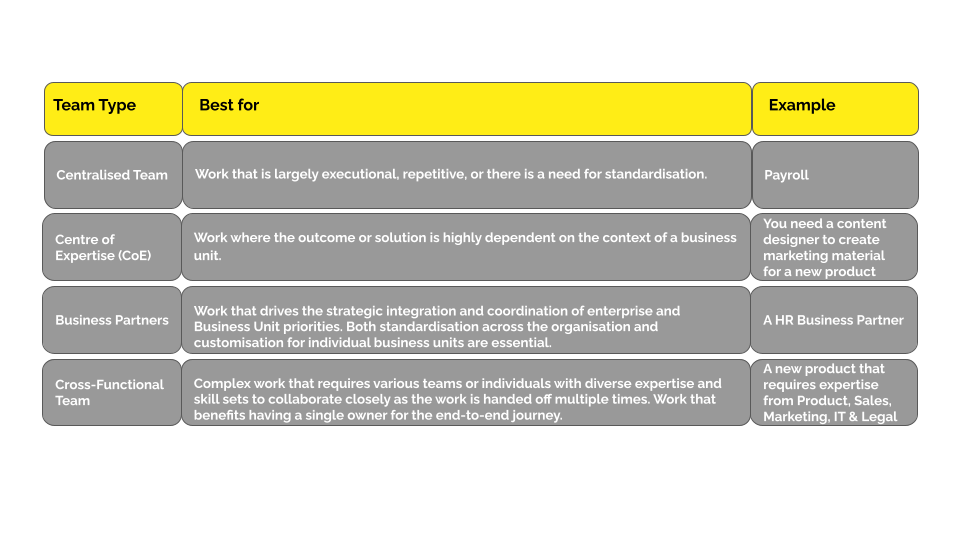
- Team Types: A category of teams for individuals who are homed together based on what work they do, where they sit and who directs their work.
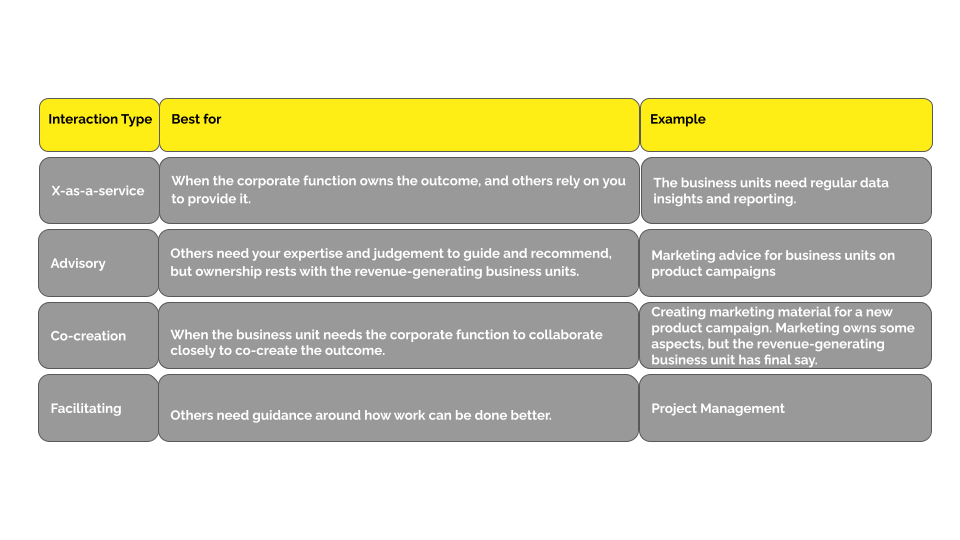
- Interaction Types: A category of interactions based on level of control by the corporate function.
Team Types
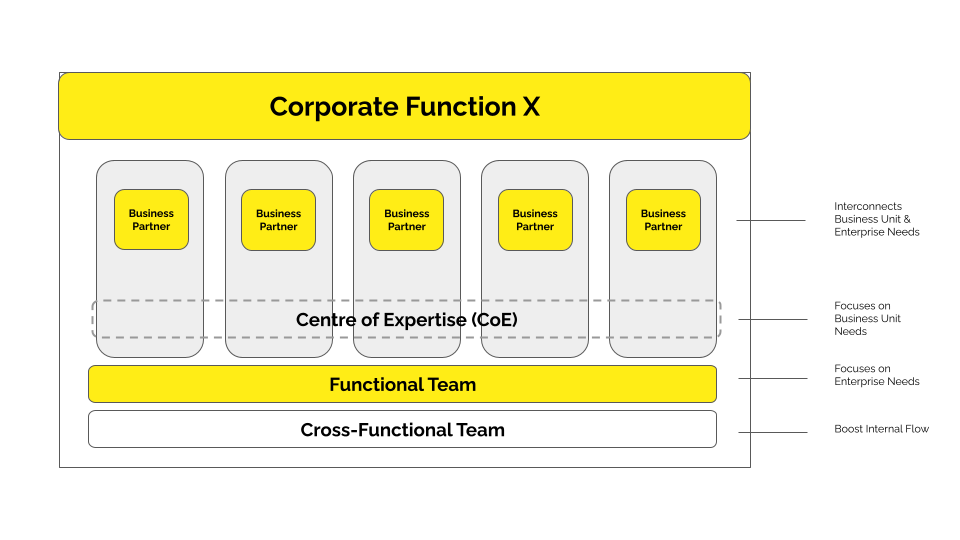
For Corporate Functions, the Radically Teaming Model has four different team types.
Interaction Types
The Radically Teaming Model has four interaction types, which define how the four teams above interact.
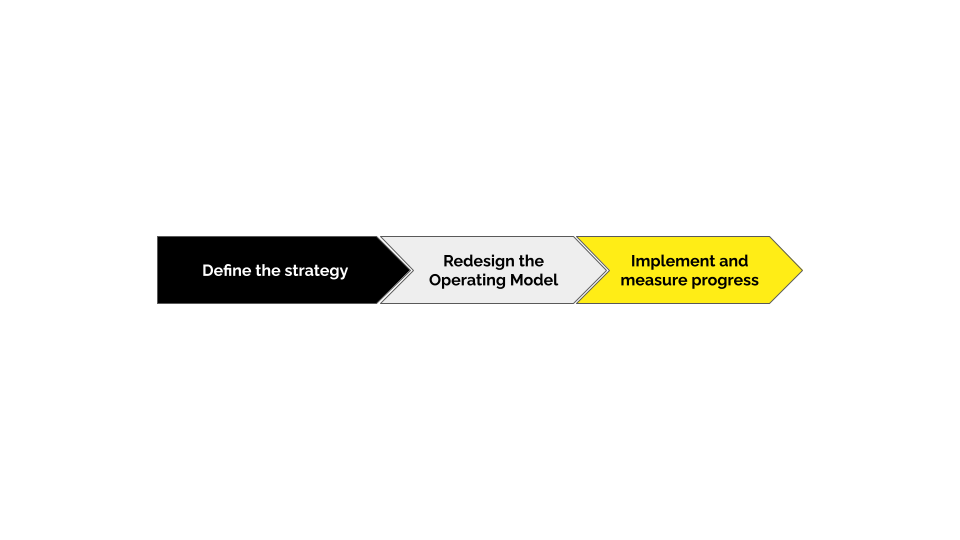
Designing the Operating Model
We take a co-creation approach to design, leveraging the Radically Teaming Model. We believe you know your business better than anyone, and by collaborating with our highly experienced team of experts, we can co-create a model that works for your specific situation.
Clarity on the strategy is always the starting point as an operating model brings strategy to life. Given the enabling nature of corporate functions, this can be as simple as defining how it will support the organisational strategy to achieve its goals.
While structure is often the most visible part of the operating model, its harmonisation with governance, ways of working, future capabilities, and leadership and culture determines how well the organisation’s strategy is translated into results.
Embedding the new operating model requires focus, tenacity, and patience. With guidance, teams will mature as they build a rhythm in the new processes, gain confidence in decision-making, and feel ownership of their work. This will ultimately increase the speed of delivery and build an adaptive culture.
If you are considering an operating model change, discuss partnering with us on your journey.
Contact edwin@radically.co.nz