Many self-managing teams struggle to reach a truly high-performing state. When an organisation moves to a self-management model, a key service centralised management traditionally played – giving feedback – is often ignored, leaving teams struggling to truly grow. In this article, we share how to give effective feedback to improve both team and individual performance.
Models for high-performing Teams
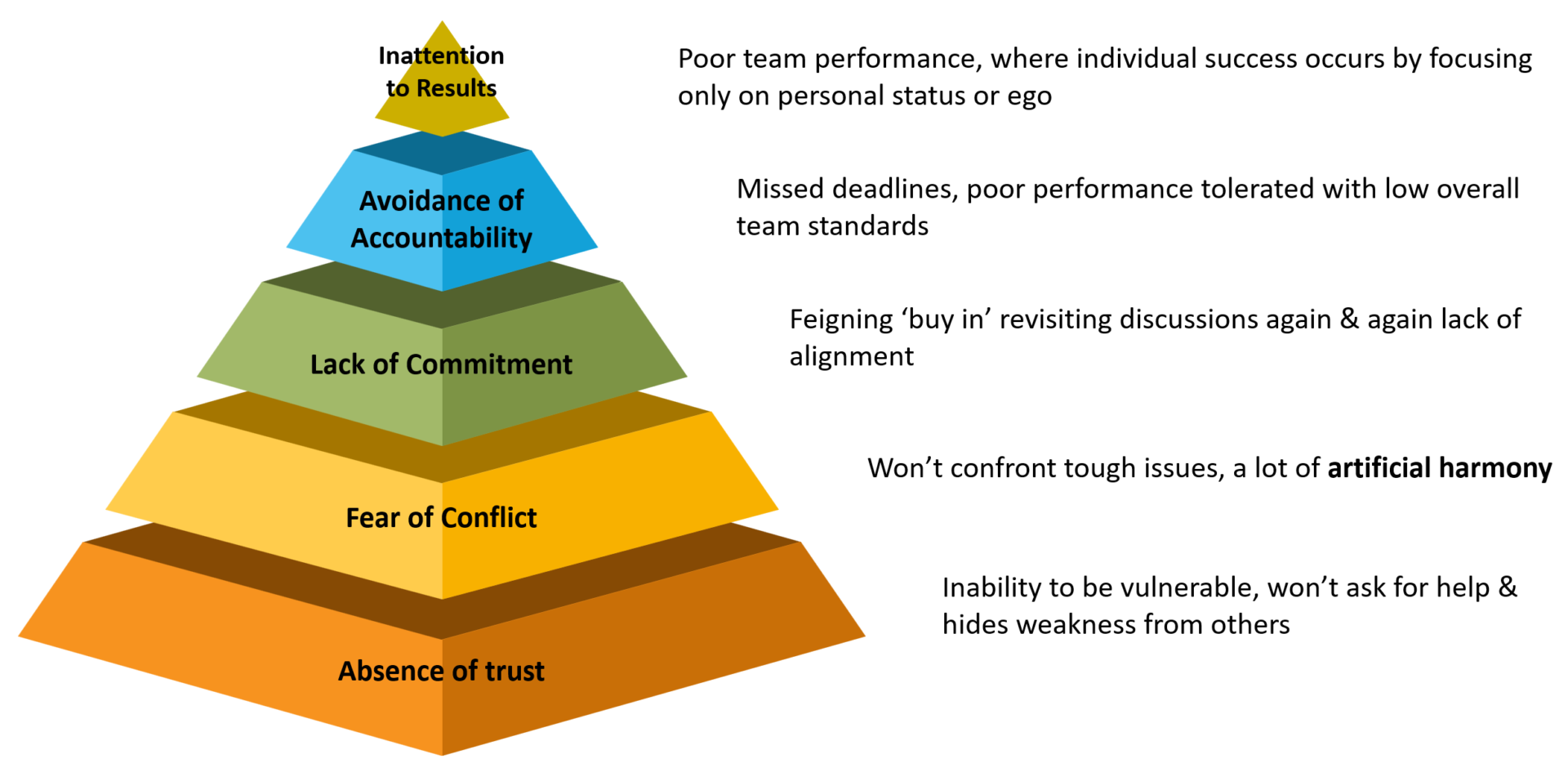
There is a clear and obvious pattern across the models for high-performing teams. Dr Patrick Lencioni’s 5 Dysfunctions of a Team says the trust and the ability to productively process conflict are critical foundations. Trust is built on being vulnerable, being prepared to ask for help and not being afraid to make mistakes in front of others.
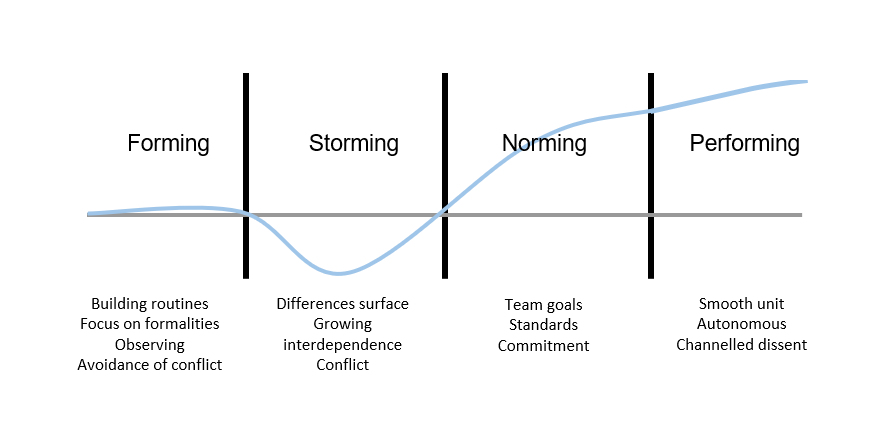
In addition to this, Tuckman's model shows the importance of keeping a team together to give them the opportunity to work through the stage he called Storming. This is where differences surface and they learn how to process conflict productively.
The result of this is a set of team norms that guide how the team works. Eventually, when a team stays together long enough to build on these norms, it can increase performance. Productivity often suffers during Storming as they learn how to manage conflict and truly become a team.
Google’s Project Aristotle made another significant contribution. In one of the largest studies of its kind, Google gathered some of their best statisticians, psychologists, sociologists, engineers, and researchers to try to understand what makes a high-performing team. They found Psychological Safety was the single most important factor. An individual’s belief that it is safe to take risks and be vulnerable in front of their teammates was the most important factor of all.

It turns out trust matters big time.
“There’s no team without trust” - Paul Santagata, Head of Industry at Google
While this work is a major step forward in what we need to create high performing teams, the question of how to do it is often left unanswered.
An approach we take at Radically is to help our clients develop a culture of feedback.
How to give effective feedback
Many organisations we work with have no consistent approach, training, or support for their people how on to give effective feedback. We believe this inhibits a critical feedback loop in individual and team development. When feedback is given, it is often clumsy, sugar-coated or worst of all, toxic. When it is received, it is often painful, upsetting and manipulative.
There are better ways! It just requires practice and support.
A useful starting point is Radical Candor – a model developed by Kim Scott during her time at Google. The model is really simple, which is one of the reasons we like it.
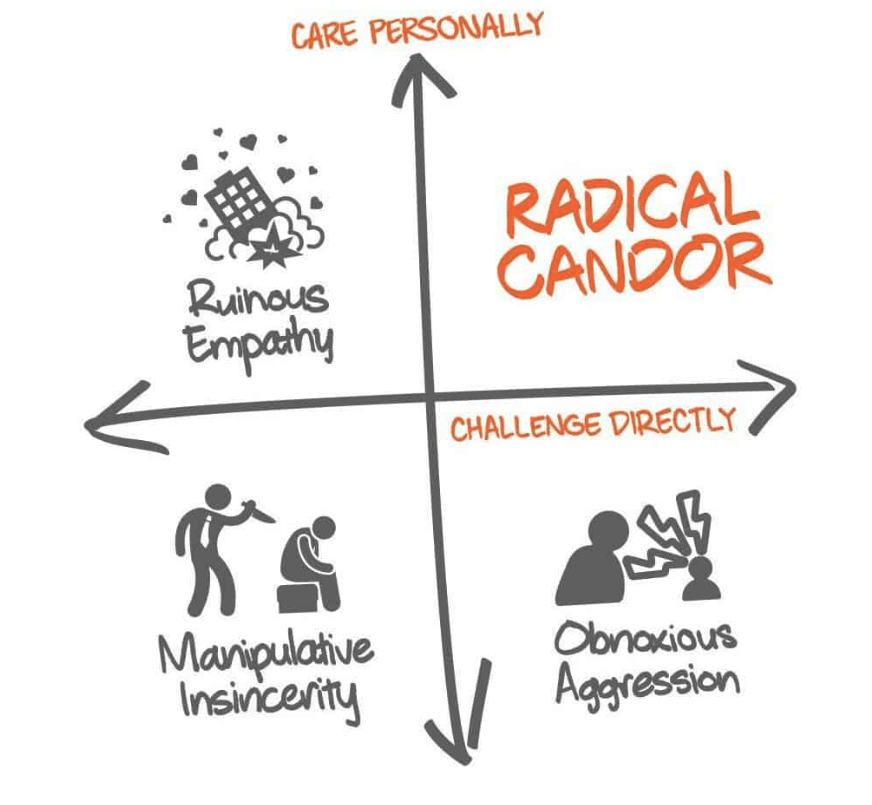
The way we use it is to first assess your intent on the Y-axis. Do you care about the person you are giving feedback to? Be honest with yourself. If you are in the bottom two quadrants, then you are better to keep silent and take some time.
Assuming you are on one of the top two quadrants, you now need to decide whether you will “be nice and say nothing”, or whether you will be honest with them. In my experience, this is where most people come unstuck. They tell themselves “best say nothing” or “I will just avoid working with them next time”. This isn’t helpful.
Kim Scott suggests you start your feedback by showing you care personally. Think about the benefit for the receiver and position it this way. Example – “I know you do a lot of public speaking, and this is an important area of your career, so are you open to some feedback on some suggestions I have?”
In my personal experience, you genuinely need to care about the person and want them to do better. If you don’t, it shows through and feels hollow.
Now share the feedback
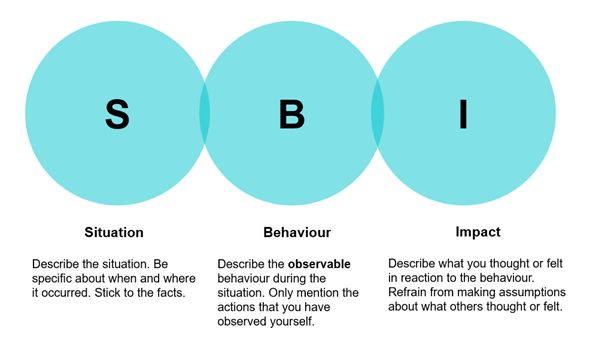
The next step is to share the feedback. This introduces the second model we use extensively, again because of its simplicity. The Situation-Benefit-Impact (SBI) model is a fantastic way of constructing the feedback in a way that focuses on the problem, not the person.
It helps you structure your feedback into
- The specific situation - when was it, during what part, who was there, what was going on.
- The behaviour you observed. What did the person say or do?
- The impact – what was the impact on you from the behaviour. This is the part that is impossible to argue with because the impact is the impact you felt.
Here is a good example:

Notice how the situation, behaviour and impact are clear and specific. The impact also doesn’t pass judgement. It simply expresses the giver's concerns.
Also notice how the feedback focuses on the problem, not the person. That is the entire objective, and it now gives you an opportunity to work together to address the problem.
Finally, use curiosity. You can’t assume you are right and they are not. There may be many other factors involved. Here is how:
- Adopt a learning mindset, assuming you don’t have all the facts. State the behaviour as an observation.
- Engage them in an exploration discussion. For example, “I imagine there are probably a few different factors at play. Perhaps we could uncover what they are together?”
- Ask for solutions. The other person may well hold the key to growth. Ask directly, “that do you think needs to happen?” Or, “wow could I support you?”
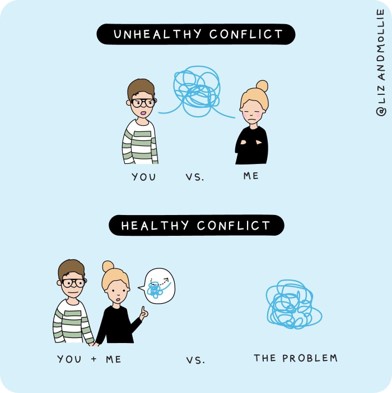
By shifting our energy away from unhealthy conflict, to solving the problem, trust is built. As per the high-performing team models - it is safe to take risks and be vulnerable in front of my teammates.
Don’t forget positive feedback
While feedback on areas to improve is important, just as important is feedback on areas where someone is doing well. But in what proportion?
Research suggests there’s a golden ratio for high-performing teams. The ideal positive-to-negative ratio is 5:1. Meaning, for every piece of feedback about something that to improve, you need to share five positive comments as well.
The research showed
- high-performing teams has a 5:1 ratio
- medium-performing teams 2:1 ratio
- low-performing teams had a 1:3 ratio meaning three times as much negative feedback as positive.
Positive feedback is important! Here is another example.

How to bring effective feedback to life
Now that you know how to give effective feedback, you need to make it a habit. The way we tend to do it is to mentor individuals and teams using both Radical Candor and SBI. At first, it requires time together to work through how they give the feedback effectively, and perhaps even practice together, but like most things, practice makes perfect.
What to watch out for
When we first established Radically, we set out to create a strong feedback culture. Along the way, we learned a lot of important lessons and it is fair to say there are definitely some gotchas to watch out for. Here is what we learned:
- There is such a thing as too much feedback! We got to a point where it all became a bit overwhelming and we had to tone it down. Some of us had moments of “for goodness sake – enough with the feedback!” Each organisation needs to find the right balance for them. Inspect & adapt.
- It is okay to say no. We always ask if someone is open to feedback and if they say no then you need to respect that. Sometimes people might be having a bad day or going through tough times elsewhere in their life and now is simply not the time.
- Culture, upbringing and mental models impact people’s attitude to feedback. For example, many of us Kiwis have been raised in a culture of Ruinous Empathy. We are generally a kind bunch, but we are very indirect. We prefer suggestions, hints and innuendo over directness. Overcoming this can feel very uncomfortable. Other cultures are comfortable being more direct as this is normal. Others still tend to be hierarchical and would never give feedback to a more senior person. These are all challenges to discuss with your people and work through. Find what works for you.
- SBI can be weaponised. I have seen SBI manipulated into “when you do this is makes me feel like that” with the implication that you need to stop what you are doing. In one situation many years ago, I had to give feedback to a consultant who had gone to the client site dressed inappropriately. He said, “when I have people tell me what I can and can’t wear it challenges my belief system and makes me feel anxious. The impact on me is that I need to take the rest of the day off.”
- Timing is everything. Sometimes, impromptu feedback is best. If the moment is right and the situation has just occurred, that can be the right time. Other times, it is better to stop, wait and think it through. This is all down to your own professional judgement.
- Feedback isn’t just a tool or practice – it is a culture. An organisation is a living, Complex Adaptive System where the system influences the behaviour, and the behaviour influences the system. For change to be successful you need to influence both. There is no point in expecting a certain behaviour if your system does not encourage or reward it. This is why we try to focus on a culture of feedback, not just a practice or tool.
Finally, there is also an art to receiving feedback. During our “too much feedback” crescendo, I wrote this guide on how to receive feedback for all the Radically team. I have now published this as the sister article to this.
Do you have experience on how to give effective feedback? How has it worked for you and what challenges did you experience? Please feel free to share in the comments below so we can learn and grow together!








