You probably don’t have to look very far to find people facing problems in their personal life or at work. They find themselves in a challenging situation and struggle to find a way out. Often times they are too focussed on all the negative things that are happening.
Attempts to solve the problems, even when acting with the best intentions can end up having the opposite effect, leaving the person feeling worse. One of the most valuable things you can do as an individual is to counterbalance that negativity. First, we need to understand how the negativity is created and sustained before we can break out of it.
A few years ago, one of the teams at my company was struggling to keep up with the delivery of their project, with tight deadlines to be met. the Product Owner, new in the role, was under a lot of stress from the demands of the Account Manager. The Account Manager was adamant in meeting deadlines for the client and was continuously applying pressure to the team. Stuck between the demands of the Account Manager, and the development team not keeping up, the Product Owner felt overwhelmed and spent their days keeping busy with low priority work. They shied away from hard decisions and complaining about the unfairness of their situation to other people at the office.
The situation worsened as time went on, until one of the senior managers became aware of it. After talking to the Product Owner they decided to help out by creating a delivery plan to have more alignment between the Product Owner and Account Manager. And so, Product Owner felt an immediate sense of relief. The intervention of the Senior Manager seemed to have taken off some of the pressure coming from the Account Manager. However, the relief was short-lived and the Product Owner quickly started feeling even more insecure.
I believe it’s safe to say that we have all found ourselves in situations where we felt trapped and without a way to move forward. In the end, we think of all the reasons and people responsible for our misfortunes. We just hope that someone would finally do something, anything about it. Or maybe you are the one finding yourself having to constantly step in and take over the situation to get to a positive outcome.
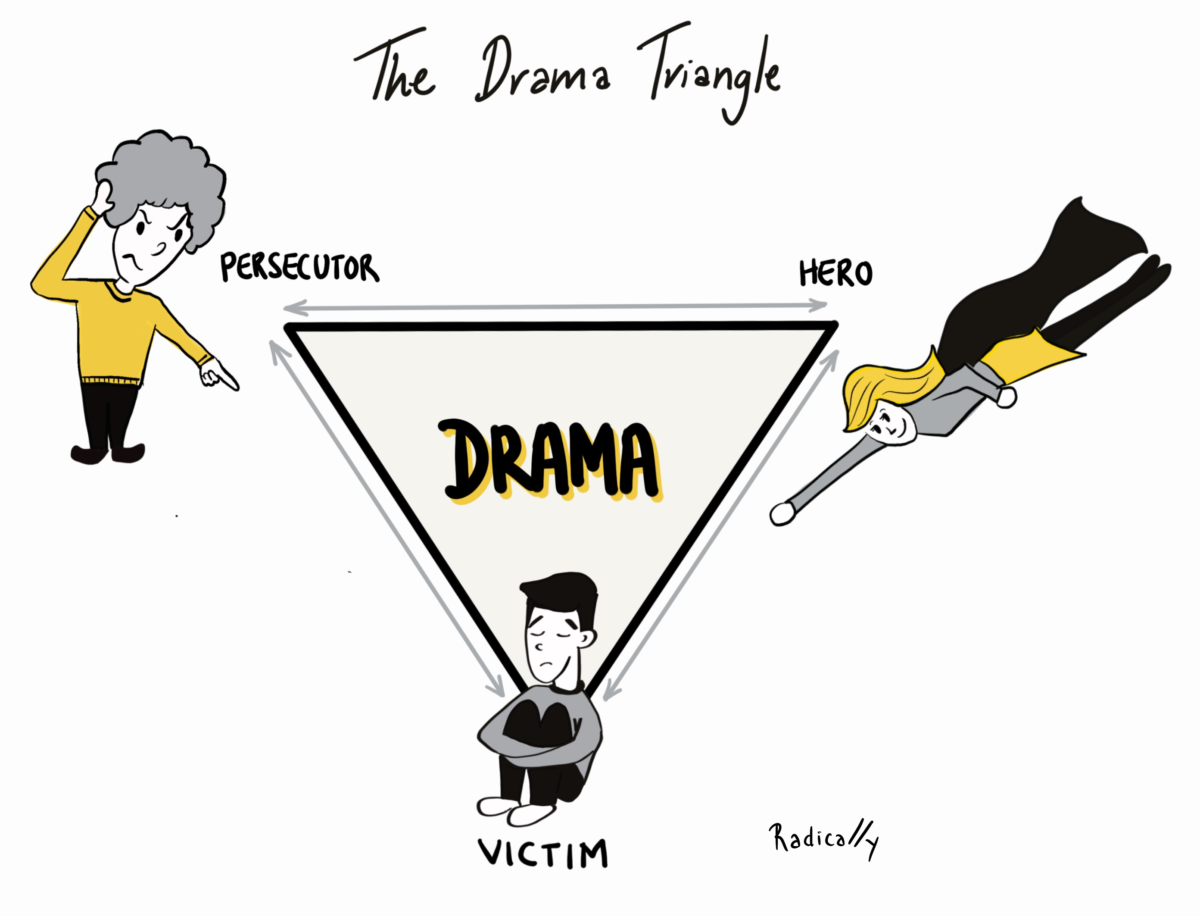
Stephen Karpman describes these situations in his Drama Triangle. Let's take a closer look at the various roles at play.
The Drama Triangle
In our story, the Product Owner falls into the role of the Victim. They feel as though things happening to them are largely out of their control, leaving them feeling helpless and disempowered. They feel trapped and unable to act on their own, avoiding facing the necessary challenges, looking for someone or something to get them out of that situation.
The Account Manager takes on the role of the Persecutor. They are the perceived cause of the Product Owner taking on the Victim Role, and being helplessly trapped in that situation. The word “perceived” is key here. The Victim might view the Persecutor as the source of their hardship and misery, but that doesn't mean it's true. While the Persecutor in our story is a person, this role might also take the form of a specific situation. For example, it might be a co-worker, a boss, a spouse, or a parent. Or it can be a situation like a deadline, the realisation of not meeting your target, financial struggles or even a natural disaster.
The final piece of the Drama Triangle is the Hero role, also called the Rescuer or Saviour. The Hero intervenes on behalf of the Victim in an attempt to save them from the Persecutor, much like our Senior Manager created a delivery plan for the Product Owner. This role of the Hero is tricky because initially, it might not seem like there's anything wrong with stepping in and fixing things. However, the result is that the Hero reinforces the Victim attitude. Their actions underline the helplessness and disempowerment of the Victim and reinforce the perceived persecution.
While the Senior Manager created an initial feeling of relief for the Product Owner, who was grateful for their help. In the end, the Product Owner was left with a deeper feeling of self-doubt and anxiety for the next project. Wondering if someone would need to step in yet again. Like the Persecutor, the Hero can either be a person or a situation, like winning the lottery.
As you can see, all three roles are closely related and keep reinforcing each other. Continuously showing up as a Persecutor reinforces the Victim stance, and a Victim will continue to wait for their Hero. With time, these behaviours create a downward spiral of unhealthy dynamics.
Luckily, it’s possible to break this downward spiral and replace it with a much healthier alternative.
The Empowerment Dynamic
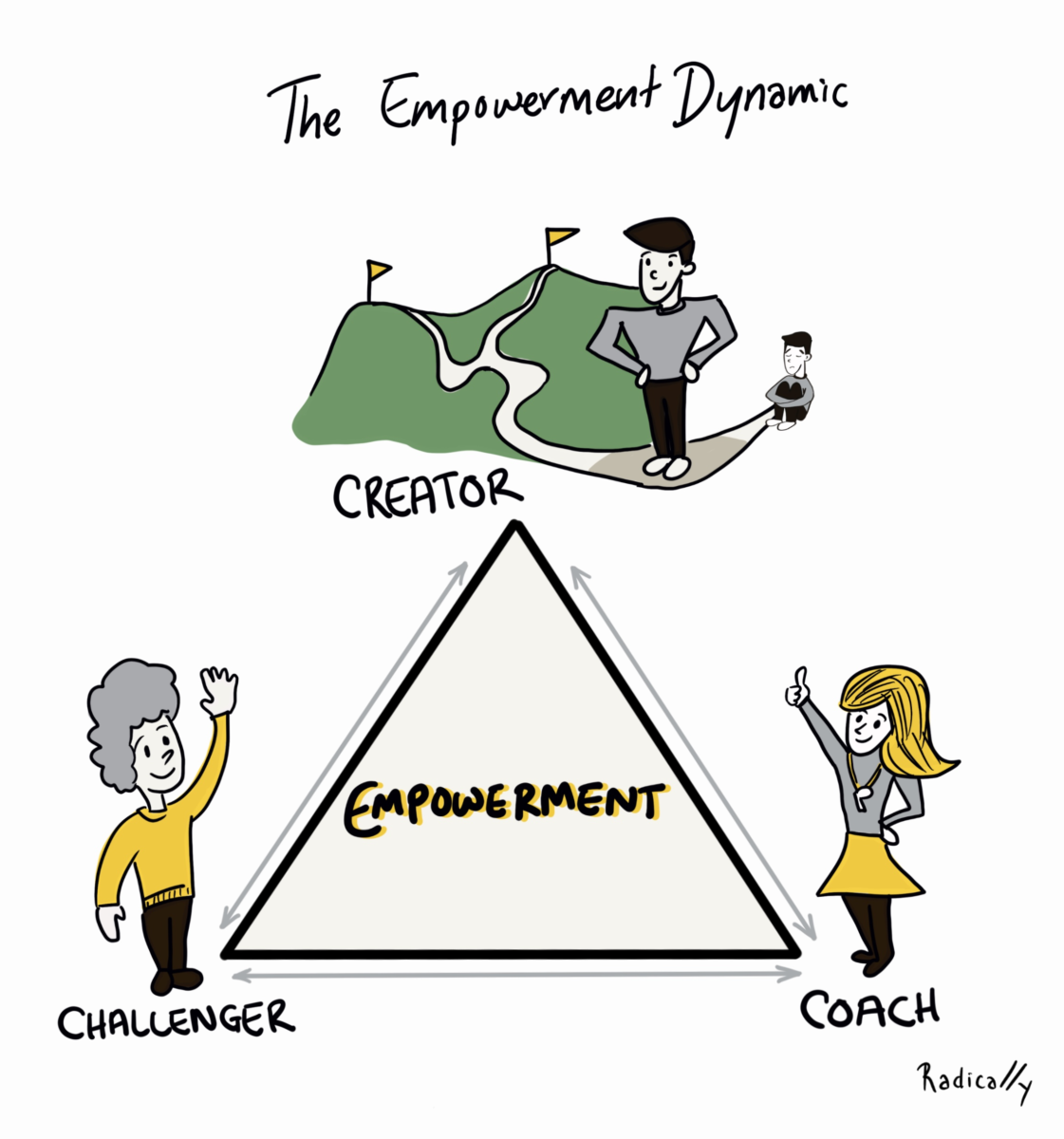
In his book “The Power of TED” David Emerald describes a response to the Drama Triangle called the Empowerment Dynamic, and dives into how we might make the switch to it. As with the Drama Triangle, there are three roles.
In place of the Victim, we have the role of the Creator. A Creator, rather than feeling helpless, realises that they have much more power and possibilities for action. They are able to choose a response to their circumstances and can find a way forward. They are focused on opportunities rather than problems, and are motivated by passion and their enthusiasm about bettering their situation and themselves. For example, our Product Owner might have sought input and collaboration with the Account Manager, or proactively gotten some advice from senior management.
The role of the Persecutor now becomes the Challenger. As a Challenger, the role is about triggering the Creator's ability to make things happen. They might encourage them to learn new skills, make difficult decisions and do what's necessary to get the desired outcome. They surface possibilities for the Creator to grow, like an Account Manager, highlighting risks and communicating needs transparently with the Product Owner.
In the final role, the Hero becomes the Coach. A Coach, instead of fixing or solving things for the Victim, sees people in charge of their own actions and the owners of their outcomes. In addition they facilitate personal progress and offer support by showing pathways, offering perspectives and giving advice. In our story, this is where the Senior Manager could have made a real impact, by providing the Product Owner with the tools and knowledge required to build their own delivery plan.
Making the shift to empower your team
Like in the Drama Triangle, all three roles of the Empowerment Dynamic are closely connected and reinforce each other, but they create much healthier dynamics. Luckily, making the shift can be initiated by any of the three roles.
Starting to show up as a Creator will eliminate the perception of a Persecutor by acknowledging opportunities and challenges. This redefines the role of the Hero since there is no one to be rescued. Rather someone in need of support and perspective. As a Challenger, constructively surfacing opportunities and triggering growth will not leave people feeling like powerless Victims needing a Hero. Moving away from Hero behaviour to a supporting coaching approach will empower people to own their own actions and outcomes. Helping them see their perceived Persecutor as an opportunity to grow.
Whichever role you might be playing in a Drama Triangle, shifting to a healthier dynamic starts with a realisation. Only you can change your own thinking and behaviours, and that it needs to be a conscious choice.
If we want to change something about our lives, we need to start thinking and acting differently today. Rather than wait for situations or people to change tomorrow.
Having worked with many different leaders and teams over the years, I’m aware that recognising the detrimental patterns of the Drama Triangle can prove to be difficult while being in the midst of it. It can be even more difficult trying to make the shift to the Empowerment Dynamic without support. At Radically we help leaders and teams recognise harmful dynamics and support the shift of mindset and behaviours, to create an outcome focussed, collaborative culture.