The phrase "one bad apple spoils the barrel" implies the undesirable behaviour of one person can spread to others, impacting the performance of an entire team. Many have experienced this phenomenon, feeling like their team is falling well short of its potential. But is there any evidence supporting this phenonium? A fascinating study has shown that indeed, a single, toxic team member can create group-wide dysfunction and breakdown.

The Toxic Blend: How One Rotten Apple Spoils the Barrel
We have all worked in teams where there is that one “difficult” person. They often display a lack of respect for their colleagues, disregard for team goals, and have an unwillingness to take responsibility for their actions. They may engage in gossip, create conflicts, and foster a hostile work environment.
They seem to consume a disproportionate amount of time and energy. Conversations with them feel “heavy” and they tend to sap your energy. There are many common examples - The Brilliant Jerk, The Controller, The Slacker, The Anti-Establishment Person, The Career Politician, The Passive-Aggressive.
The Impact of Toxicity on Team Dynamics
Often teams don’t have any choice but to do their best and simply tolerate the difficult person, citing personality eccentricities, often with a roll of the eyes. The impact can be severe, ranging from reduced morale, increased stress, burnout, turnover, low levels of creativity and problem solving, along with reduced productivity.
The negative influence of a toxic team member can spread like wildfire, causing dysfunction in the entire group.
- Simon Sinek
The Toxic Team Member: A Catalyst for Chaos
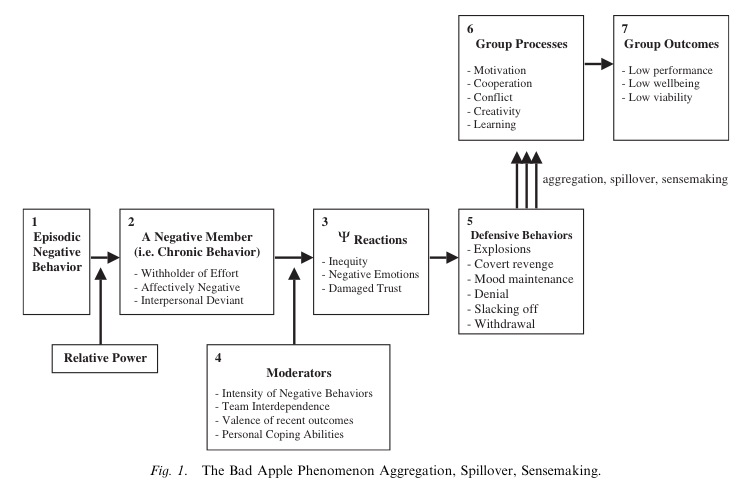
Will Felps, Associate Professor of Organization & Personnel Management at Rotterdam School of Management, published a fascinating paper titled How, When, And Why Bad Apples Spoil The Barrel: Negative Group Members And Dysfunctional Groups. The paper discusses how, when, and why the behaviours of one negative group member can have a powerful, detrimental influence on an entire team. In other words, how one bad apple can rot the barrel.
Felps conducted a social experiment. He took groups of four college students and arranged them into teams. Each team had to compete against the other to solve some management problems. Unbeknown to them, Felps planted an actor in each team, designed to feign one of the three personality types Felps suspected caused major issues:
- The Depressive Pessimist - will complain that the task that they're doing isn't enjoyable and make statements doubting the group's ability to succeed.
- The Jerk - will say that other people's ideas are not adequate but will offer no alternatives himself. They'll say "you guys need to listen to the expert - me."
- The Slacker - will say "whatever", and "I really don't care."
The existing research assumed that groups had the ability to overcome bad apples and the power of the group would override the bad apple forcing them to change their behaviour. However, Felps findings proved otherwise.
Groups with a bad apple performed 30 to 40 % worse than groups without a bad apple. The ability to get along, share work and collaborate significantly dropped in groups with a bad apple.

The Domino Effect: From Toxicity to Dysfunction
In groups with a bad apple, other team members begin to take on the bad apple's negative behaviour. When the bad apple actor acted out one of the three personalities, the other team members started to act in the same way. When the actor was a jerk, other team members would begin acting like a jerk. When the actor was a slacker, they began to slack, too. Even worse, they didn’t just act this way to him – they acted this way towards all other team members. The bad behaviour had a ripple-on effect, propagating that type of behaviour throughout the team.
This is an immensely important discovery. One bad apple can cause rot in the entire cart by altering the behaviour of everyone.
Interestingly, there was one exception in the experiment. One group performed well, despite having a bad apple. The difference? This group had a leader with strong skills in diffusing conflict.
Psychological Safety
Harvard Business School professor Amy Edmondson identified psychological safety as a cornerstone of effective teamwork and organizational success. Psychological Safety is a vitally important part of our consulting work at Radically.
Edmondson defines psychological safety as “a shared belief that the team is safe for interpersonal risk-taking." Project Aristotle, an initiative at Google, sought to uncover the dynamics of successful teams and identified psychological safety as one of the key factors driving high-performing teams. They found psychological safety was more impactful than the next four factors combined.
However, a culture of psychological safety isn't just a leader's job - it is everyone's responsibility, especially as organisations become more decentralised and self-managed.
Restoring Harmony to Rebuild a Dysfunctional Team
So if undesirable behaviour can damage teams, and it can spread, what can we do about it?
There are broadly two key ways to approach this - by developing a group's ability to self-manage this and through people in leadership and management roles supporting this. the combination of both is the most successful approach.
The Power of Teamwork
Humans naturally form social group norms to guide behaviour. Norms take shape and change over time as the group evolves. Often group norms are implied and unstated, detected through the day-to-day interactions with others.
One way to help bring this into focus is to establish a team charter. This preventative action involves a team defining their desired values and behaviours. It can be quickly achieved with little more than a flipchart and some markers, using prompts such as
- What would make our team powerful?
- What can we count on from each other?
- How do we want to be when we are challenged?
A team charter provides a clear statement of expectations - that is, what good looks like. If behaviour slips off track, the group's role is to call each other out and self-moderate. However, this assumes the group has the capability and experience to do this. enter the leadership role.
The Role of Leadership
A good leader will help a group retain ownership of their behaviour and step in if it becomes unsafe or they see the group struggling with a lack of skills and experience.
A technique I frequently use is to help the group "notice" their behaviour if it differs from what they said was important in their team charter. The way you do this is very important. Avoid assumptions and embrace curiosity: "I am noticing that [observation]. Do you notice that too or am I misreading the situation?" If they agree, I might facilitate a discussion on what happened and what we can learn from this to improve. Note at no point am I taking ownership. The group is accountable for their behaviour. Reveal dont resolve.
Motivational interventions
Felps calls these “motivational interventions” - acts of teammates that attempt to change negative behaviour via influence. His research shows this is an effective way to deal with The Slacker and The Brilliant Jerk, but is less successful with the Depressive Pessimist. Most people do not have the techniques required to resolve a teammate’s negative moods, and so tend to simply avoid or reject them. This is where a different leadership stance kicks in. Rather than facilitating (which is for a group), a personal coaching stance would probably be a better choice. In other words, connect with them, empathise, share how you observe their behaviour impacting the group, and help them consider some options to move forward.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of a toxic team member carries profound implications for group dynamics and team performance. The fascinating study by Will Felps has provided valuable insights into the impact of a single toxic team member on an entire group. This research has shown that the negative influence of such an individual can indeed spread like wildfire, leading to reduced morale, increased stress, burnout, turnover, and decreased productivity within the team.
Moreover, Felps' experiment shed light on the domino effect of toxicity, where other team members often begin to adopt the negative behaviour exhibited by the bad apple, causing a ripple effect of dysfunction throughout the group. This discovery underscores the critical importance of addressing toxic behaviour promptly and effectively.
Psychological safety, as highlighted by Harvard Business School professor Amy Edmondson, emerges as a vital factor in promoting effective teamwork and organizational success. It is essential for fostering an environment where individuals feel safe to take interpersonal risks, contributing to high-performing teams.
To counter the detrimental impact of toxic team members and restore harmony within a dysfunctional team, there are two key approaches: empowering the group to self-manage behaviour and leveraging leadership to guide and support the team when necessary.
Motivational interventions, as described by Felps, offer a powerful tool for addressing negative behaviors, especially when coupled with a coaching stance that emphasizes empathy and constructive feedback.
In summary, the study by Will Felps and the broader discussion surrounding toxic team members emphasise the importance of fostering positive group dynamics and addressing negativity promptly. By promoting psychological safety, establishing clear expectations, and combining self-management with effective leadership, teams can mitigate the influence of the "bad apple" and work together harmoniously to achieve their goals and reach their full potential.
If you are interested in learning more about Will Felps work, listen to this recording from the “This American Life” show. It’s an absorbing interview with Felps.
